Do you intend to construct your own computer? You can’t just look at a computer and know what kind of motherboard you need, so picking the best one can be difficult. The only difference between these motherboards is their size, but this assumption is completely false.
We’ll be explaining the many ways in which these motherboards vary from one another. What you intend to use the motherboard for is the primary consideration. These mainboards were developed with the end product in mind from the start.
Bạn đang xem: Motherboards Atx Vs Micro Atx Vs Mini Itx Update 03/2026
Let’s take a look at how big these motherboards are before we continue.
ATX: 305 x 244 mm (12 x 9.6 inches).
Micro ATX is 244 x 244mm (9.6″ x 9.6″) in size.
Mini ITX is 6.7″ x 6.7″ (170 x 170mm).
PC Motherboards: The Basics
Intel developed and debuted the ATX form factor in 1995. The ATX standard has been the go-to for desktop computers for almost 25 years.
ATX is the largest of the three motherboard sizes we’re considering, with dimensions of 12 by 9.6 inches. All ATX motherboards are required to conform to this size standard. Mounting holes, an input/output panel, power outlets, and other interfaces are all pinpointed for you.
All of these components are required for any modern motherboard. The motherboard will not come into contact with the case’s metallic surface thanks to the mounting points. The computer’s display, audio, and USB ports are located on the back, and you can get to them with the help of the I/O panel and shield. Power plugs and other interfaces need to be in standard locations to ease the work of system integrators.
Nonetheless, an ATX-sized motherboard isn’t for everyone, especially if a smaller final product is the aim. MicroATX boards, measuring only 9.6 by 9.6 inches, are here to save the day. The standard specifies the various critical points that must be met, just as it does for larger ATX motherboards.
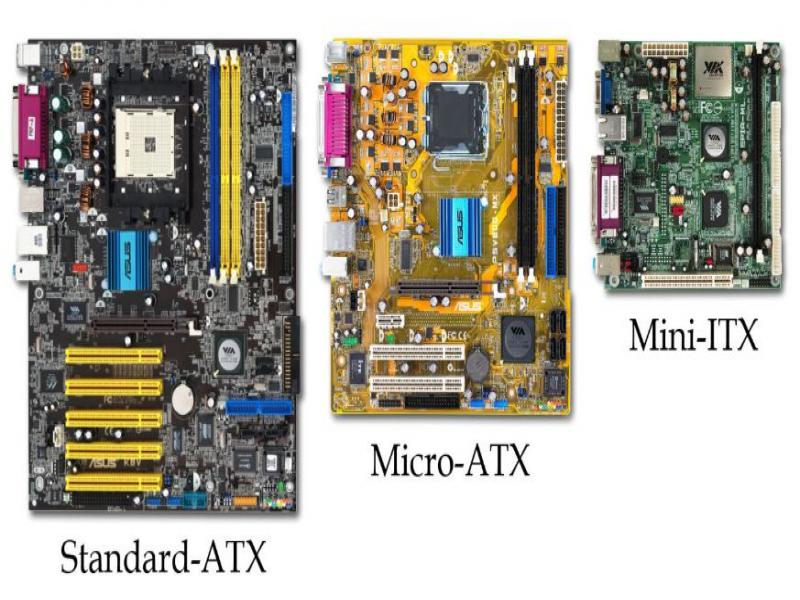
Finally, in 2001, Via Technologies introduced the Mini-ITX, the world’s smallest computer motherboard at just 6.7 by 6.7 inches.
You can add more components to an ATX motherboard. They typically have six PCI Express slots at most, where components like video, audio, and network adapters can be installed. The article’s focus is on standard ATX motherboards, but there are also Extended ATX (or EATX) boards with seven PCIe slots, which are more appropriate for enthusiasts and servers.
The Mini-ITX only has room for a single PCIe slot, while the MicroATX can accommodate up to four.
ATX vs Micro ATX vs Mini ITX
When comparing these dimensions, it becomes clear that the ATX motherboard is the largest, followed by the Micro ATX and the Mini ITX. The ATX and Micro ATX motherboards both measure.1 inches in width, and they look nearly identical to one another.
These motherboards are otherwise identical, with the exception of their length. The additional space for PCIe slots is why an ATX motherboard is longer. More PCIe expansion cards are being added to the system. As opposed to its rivals, the Mini ATX is both compact and inexpensive.
First, let’s review the features and specifications of these motherboards, and then we’ll discuss their advantages and disadvantages.
ATX Motherboards
If you plan to construct a workstation or a powerful gaming cpu, an ATX motherboard is your best bet. The four RAM slots found on ATX motherboards give you plenty of room to upgrade your computer’s storage capacity. A maximum of 32 GB of RAM can be installed in each available slot.
It may seem like a lot, but many benchmarks and tests have shown that there is no discernible difference between 8 GB and 16 GB ram when it comes to performance and frame rates in games. However, if you’re a programmer or intend to use this PC for your work, not even 32 GB of memory will be enough.
Ram’s extensive apps are a common source of frustration for developers because of the resulting PC slowness. This motherboard’s support for Multi-GPU and other PCIe cards is another notable feature. It has 7 PCIe Slots. Most motherboards do not have this function.
The ATX standard ensures top-notch performance in every area and allows for numerous PC enhancements. These motherboards support a wider variety of upgrades than their competitors but come at a higher price and larger size.
The advantages and disadvantages of ATX motherboards are briefly discussed below.
THE PROS
Increased Number of PCI Express Slots
Superb Playing Conditions
With support for up to 4GB of RAM, this is the best option for power users.
THE CONS
Extremely Sizeable
The Highest-Priced Motherboard on the Market.
Micro ATX Motherboards
If you’re on a tight budget but still want to build a gaming PC, the Micro ATX motherboard is your best bet. All but the number and size of PCIe slots set the Micro ATX motherboard apart from its ATX counterpart.
You won’t have to worry about running out of memory with a micro ATX motherboard because it supports up to four RAM slots. The fact that this motherboard is less expensive than its two main rivals is undoubtedly its biggest selling point. Micro ATX motherboards are the industry standard, and for good reason: they pack all the bells and whistles a gamer could want into a tiny package.
Without Multi-GPU support, these motherboards are not a good fit for anyone planning to construct a PC with more than one graphics processing unit (GPU). Because of its compact size, the Micro ATX motherboard is compatible with a wide variety of cases. Although the reduced size reduces the number of included features, it may provide more room for personalization.
Xem thêm : Best Mechanical Keyboard Update 03/2026
While some of the newest micro ATX motherboards do indeed support dual GPUs, they are just as expensive as their ATX counterparts, making the latter the superior choice if you require Multi-GPU support. These motherboard components are interchangeable with those found on ATX motherboards.
Have a look at the benefits and drawbacks of this motherboard to figure out if it’s something you need.
THE PROS
Slot Availability in RAM
The Top Pick for Low-Cost Play
Compared to its rivals, it is both the cheapest and most in-demand option.
In terms of size, this motherboard is compatible with virtually all cases.
THE CONS
Multi-GPU configuration is not supported.
It’s a hassle for the user to install additional PCIe components like sound cards, etc., because there aren’t enough PCIe slots.
When compared to a standard Micro-ATX motherboard, the price of a new model that supports multiple graphics cards is prohibitive.
Mini ITX Motherboards
Mini ITX motherboards are the most compact option for those who need a lightweight, transportable computer. Due to the Mini ITX’s limited expansion capabilities, users are limited to a maximum of 32 GB of RAM when using two 16 GB sticks in conjunction with the motherboard’s two available RAM slots.
While this motherboard would suffice for a gaming rig, it wouldn’t be up to snuff for a professional workstation. Since there is only one PCIe slot on a Mini ITX motherboard, only one graphics processing unit (GPU) can be used. Some gamers may find it acceptable if it means their PC can be smaller, but keep in mind that High-end Gaming cannot be accomplished with this motherboard type.
The price of this motherboard is higher than that of a Micro-ATX motherboard with twice as many features, which may come as a surprise to some. Due to its scarcity and high demand, this motherboard has commanded a premium price despite its compact size. This motherboard is suitable for use in the construction of a compact gaming computer. Since the components of the ATX and Micro ATX form factors are shared, this motherboard is unlike the other two in terms of its construction.
Now that we’ve established the motherboard’s overall value, let’s take a look at its pros and cons.

THE PROS
Power usage is reduced.
Being lighter and smaller makes it easier to transport your computer to new locations.
ITX motherboards are next-generation boards, so they’re compatible with the latest processors.
THE CONS
“Only 1 PCIe Slot”
Have only 2 RAM Slots
“Strange in most PC cases”
“More costly than Micro ATX Motherboards”
ATX VS Micro ATX VS Mini ITX
Then, let’s examine the relative merits of the various motherboard form factors. To begin, an ATX motherboard is the way to go if you’re looking to spend a lot of money on a high-end computer that will last you for a few years. Even in terms of aesthetics, these motherboards are leagues ahead of their micro-ATX and mini-ITX counterparts, thanks to their prevalence of high-end features like professional-grade overclocking, customizable RGB lighting, and so on.
A mid-range micro-ATX motherboard is your best bet if you want to build a cheap PC without sacrificing performance or compatibility.
Micro-ATX motherboards are the most popular choice for consumers due to their low prices and compatibility with budget cases. Mini-ITX motherboards require careful consideration to ensure you really need one, as it can be difficult to track down other parts that are compatible with them. To put it another way, if you manage to get everything together except for one key component, your final product will still be unfinished.
Additionally, the mini-ITX system selection is limited. Liquid cooling solutions may be necessary because of the poor airflow in compact cases. Mini-ITX motherboards, especially those equipped with bespoke liquid cooling systems, have a certain cuteness about them. Additionally, a mini-ITX system could be used as an HTPC system, which would look great in the family room.
ATX VS Micro ATX
Because of their widespread compatibility and impressive set of features, ATX motherboards have become the industry standard. If you want to do mainstream gaming with the right cooling solutions, it’s best to get an ATX motherboard because you can install it in most mid-tower cases. ATX motherboards are typically rectangular, while micro-ATX motherboards are more like squares. This is because different motherboards provide a different quantity of PCIe slots.
When it comes to motherboards, the ATX form factor is by far the most common, with the micro-ATX form factor being offered by a relatively small percentage of high-end boards. A high-end system necessitates an ATX motherboard.
When it comes to cost, an ATX motherboard will typically cost more than a micro-ATX motherboard, and the difference isn’t just because the former is larger and has more expansion slots. RGB lighting, among other features, are common on these motherboards. Furthermore, micro-ATX motherboards are aimed at cost-conscious customers who are looking to build a system on a tight budget. Before purchasing a full-size ATX motherboard, make sure you have a case that can accommodate it.
After that, we’ll move on to discussing general characteristics. Most micro ATX cases still have enough expansion slots to support modern video games. As there are typically only two PCIe slots on a micro-ATX motherboard, you may not be able to install a dedicated sound card, LAN card, or other PCIe devices. However, the ATX motherboards have numerous PCIe slots, allowing you to install a wide variety of expansion cards, such as NVMe cards, sound cards, Bluetooth cards, and many more.
ATX VS Mini ITX
ATX motherboards are widely regarded as the best option for powerful computers. However, these motherboards frequently fall short of other requirements, the most common of which is a smaller footprint. Because of the incompatibility of larger motherboards with smaller mini-ITX cases, an ATX motherboard isn’t a good choice if you want to construct a portable computer.
Xem thêm : How To Evolve Sinistea Update 03/2026
Because mini-ITX motherboards are so uncommon, you may have to do some digging to find one that suits your needs, and even then, it may not look exactly the way you envisioned it. The ATX form factor is used by the vast majority of mainstream motherboards, and you can find them virtually anywhere.
For the most part, a mini-ITX motherboard can be used with other small components, such as the power supply, the case, and the cooling solutions, when building a remote form factor PC. Mini-ITX motherboards are also unusual in that they typically have few features and slots for things like RAM, PCIe cards, and SATA drives.
In contrast, ATX motherboards have plenty of room for expansion cards, including memory and video processing units. For example, if you’re building a small form factor PC, you should know that mini-ITX cases can only support graphics cards that are specifically designed to fit in them, while most standard-issue graphics cards cannot be installed in a mini-ITX case. Nonetheless, a mini-ITX motherboard can be used in a mid-tower case, although this defeats the purpose of the mini-ITX form factor.
High-end ATX motherboards tend to be more expensive than their lower-end counterparts, but mini-ITX boards are in high demand as well. However, the distinctive nature of their cases means that they sell for a premium.
Micro ATX VS Mini ITX
The cost of a motherboard in the Micro ATX form factor is not significantly higher than that of a Mini ITX motherboard. Although some high-end mini-ITX motherboards do exist, both types of motherboards primarily serve the budget market. These motherboards typically cost around $100. Since most people prefer a bigger case, however, finding a micro-ATX motherboard should be much simpler. Higher-end desktop (HEDT) motherboards cost more than standard boards because they support more powerful components like Intel’s Threadripper and Extreme-series CPUs.
For the record, a mini-ITX motherboard will fit in a micro ATX case. Contrarily, a micro-ATX motherboard will not fit in a mini-ITX case. There is no difference between the power supply and any other part. Mid-tower cases typically have enough space for even the most powerful graphics cards, including those with a tri-fan design. Mini-ITX cases have a limited selection of motherboards and other parts, so if you’re looking to build a gaming PC, you’re better off going with a micro-ATX motherboard and standard-sized parts.
Micro-ATX motherboards differ from standard ATX motherboards in that they typically feature more SATA ports, allowing for more extensive storage. It is recommended to purchase a micro-ATX motherboard if you plan on using more than two hard drives.
Mini-ITX motherboards are distinctive in appearance, so if you’re looking to shake things up a bit, a mini-ITX case is the way to go. To make their mini-ITX system look even more impressive, many people use custom liquid cooling solutions and single-slot liquid-cooled graphics cards. In contrast, a micro-ATX system’s aesthetics won’t be to your liking unless you spend a lot of money on a mid-tower or full-tower case.
The biggest perk of a mini-ITX motherboard is its small size, making it ideal for frequent travelers or musicians who occasionally play shows in unfamiliar venues.
Which Motherboard Form Factor Should You Choose?
We’ll be discussing the best motherboards for your computer setup now. The Category shifts would depend on the motherboards selected for the various PC types. In that case, let’s move on to the Categories and figure out which motherboard is best for you there.
Motherboard for Gaming Computer
The Micro-ATX motherboard is a great choice if you’re a gamer who wants to build a PC for gaming. The motherboard has four RAM slots and four PCIe slots, so it can be used in any case. It also supports all the components and upgrades necessary to run today’s games. The maximum memory that can be added by the user is 64 GB, which is not even necessary for most games.
This motherboard is the best value for money if you’re looking to get into gaming on a moderate budget. These motherboards have the broadest support for the rest of the parts in your gaming PC. However, if you’re interested in High-End Gaming with support for Virtual Reality and cutting-edge technology, you’ll need to upgrade.
If you want to buy a motherboard, go with an ATX model because they support Multi-GPU installations. If you want high-end gaming, you’ll need a huge budget, but this is the way to go. However, modern gaming is best accomplished with a Micro ATX motherboard.
Motherboard for WorkStation
The ATX motherboard is the best option if you want to construct a computer for business or programming purposes. The RAM and Graphics Memory required for modern editing and rendering are enormous. This motherboard has everything you could want, with seven PCIe slots and four DDR4 memory expansion slots.
The Ram Slot supports Up to 32 GB, so you can combine 2 GPUs to get the necessary visual memory for your needs. If you need access to all available PCIe slots, this motherboard is the best option, but if that’s not the case, you’re better off with a Micro ATX board, which is otherwise identical to an ATX board except for the latter’s lower PCIe slot count.
![ATX vs Micro ATX vs Mini ITX Motherboards Comparison [Best Choice?]](https://gemaga.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/motherboards-atx-vs-micro-atx-vs-mini-itx-9.jpg)
Motherboard for Desktop Computer
Mini ITX is the ideal form factor if you want a motherboard for home or office use. Though the Micro ATX motherboard adds a lot of extra features, the PC would be quite large even with all those extras.
Mini ITX computers have a compact form factor that enhances their portability without sacrificing style. Just two memory expansion slots and one PCI Express expansion slot are present, but that’s plenty for a desktop PC. Whereas the other components might have trouble fitting inside a desktop PC, the motherboard can do so without any problems.
This motherboard costs significantly more than Micro ATX alternatives, so if you’re on a tight budget, stick with the latter. However, keep in mind that the Micro ATX motherboard’s lack of portability means you’ll need a Tower Case to house your PC.
Motherboards: When to Use What
You can build a gaming rig, an entertainment PC, or an Office 365 powerhouse with any of these three types of motherboards.
However, there are advantages and disadvantages to consider with each form factor, and we’ll discuss those next.
Gaming
The ATX form factor is the best option for first-time PC builders, with the MicroATX form factor coming in second. Because of the extra room provided by the ATX form factor, installing the various components is a relatively painless process.
While ATX is excellent, there is no reason for a beginner to avoid a MicroATX if they prefer a smaller form factor. Things are tighter than usual, but not impossible to put together. Take into account the size of the case if you decide on a MicroATX motherboard. If you’re going for a compact build, you shouldn’t use a case that is compatible with ATX. Keep in mind that the width of some MicroATX cases exceeds that of ATX-compatible mid-towers.
When it comes to playing video games, the Mini-ITX form factor is the “hardest” of the three due to its limited internal space. Mini-ITX boards can be used to build a reliable gaming PC, but you’ll need to give some thought to ventilation, cooling, and extra space for the graphics card. A Mini-ITX case is much smaller than a full ATX case, so you’ll need to carefully plan out what you want to put inside.
Home Theater PC (HTPC)
A Intel NUC is a great choice for a media center PC. Intel
When deciding whether or not to purchase a new piece of technology for the living room, the amount of available storage space is often the deciding factor. Mini-ITX computers excel in this scenario because they provide full-featured media center PCs in compact cases. An ATX case compatible with Mini-ITX boards is readily available for purchase. However, a smaller model is required if you plan to store it on a shelf beneath your television.
We would be negligent if we didn’t mention the Intel NUC, an even smaller motherboard. Intel’s NUC kits allow for the construction of compact PCs that don’t skimp on performance. The NUC motherboards are typically four inches by four inches, making the cases a very snug fit.
As a rule, NUCs are sold as kits that contain the motherboard, processor, discrete graphics (which can vary) and RAM. Storage and peripherals can be expanded as desired, but current NUC models do not support full-size graphics cards. So, a NUC is only a good choice if you need a PC for things like streaming video, managing your home media collection, or playing light games.
Family PC
Take what the dealer gives you. PCs for the home should be functional, but they don’t need to be super fast because you mostly just use them to watch videos online, check email, and play online games. Examine the sale prices and let those inform the construction process. Consider a MicroATX or Mini-ITX motherboard if storage space is limited.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this post has shed some light on the subject, and you’re better equipped to select the appropriate motherboard for your computer. If you found this Post helpful, we have plenty more where this came from on topics related to computers and technology.
Nguồn: https://gemaga.com
Danh mục: Blog










