While PC construction is full of acronyms and abbreviations, it’s not always easy to understand what they mean.
- Best Hide And Seek Games On PC. The Ultimate List Update 07/2025
- Best Games Like Stardew Valley You Should Play Right Now Update 07/2025
- Best Monitor For Xbox Series X And S. Everything You Need To Know Update 07/2025
- Best Gaming Setups Update 07/2025
- Best Gaming PC Under $300 – Complete Guide for Beginners Update 07/2025
Particularly now that older technologies are being replaced by newer, enhanced versions that offer better performance and, maybe, some new features on top of that.
Bạn đang xem: What Is PCIe 4.0? Complete Guide for Beginners Update 07/2025
Currently, PCIe 3.0 is being phased out in favor of PCIe 4.0 in some motherboards to make room for its replacement.
The purpose of this article is to provide a brief overview of PCIe, including its current incarnation, PCIe 3.0, and PCIe 4.0, before assessing whether PCIe 4.0 will be useful for gaming in 2022.
What Is PCIe?
Expansion cards can be connected to the motherboard using the Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, or PCIe, bus, which stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express. Graphics cards, SSDs, Wi-Fi adapters, modems, capture cards, sound cards, and more are included in this category..
It all started with PCIe 1.0 in 2003, which was the first iteration of PCI Express. PCIe 5.0 was released in 2019 and will be followed by PCIe 6.0 in 2021. Since PCIe 4.0 was published in 2013, four more versions have been released.
However, PCIe 4.0 isn’t technically the “latest” version of PCIe, but it is the most recent version to be released to the general public. PCIe 4.0 chipsets are currently only available from AMD, and it will be some time before PCIe 5.0 and PCIe 6.0 are integrated in common consumer motherboards, at least in the short term.
The number of lanes in a PCIe slot can also be used to classify them. In terms of the number of lanes, PCIe x1 is the most prevalent, followed by PCIe x4, PCIe x8, and PCIe x16.
As you might expect, more lanes mean quicker data transfer rates and better total bandwidth, and different expansion cards are designed with a varied number of lanes in mind depending on their specific needs.
![What Is PCIe 4.0 And Is It Worth It? [Simple Guide] - YouTube](https://gemaga.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/pcie-4-0-worth-it-img_6229bedcd82e1.jpg)
PCIe 4.0 Benefits
Bandwidth
PCI-Express 4.0 offers a significant boost in bandwidth, which is the primary benefit of upgrading. As a general rule, each new version of PCIe increases the bandwidth available per lane by about 20%.
Any PCIe 4.0-enabled devices can benefit from the increased bandwidth available.
Quicker storage rates (video and game loading) and faster graphics performance may be possible with PCIe 4.0-compliant devices (video games and rendering).
PCIe 3.0, on the other hand, is yet to realize its full potential in some systems. Only if you’re using a device that consumes a lot of bandwidth:
- PCIe 4.0 lanes are being used by your latest and greatest storage and video cards.
- Using PCIe 4.0 devices, which require less lanes to deliver the same bandwidth, will free up PCIe lanes.
- Ideally, your system should be future-proofed.
Storage
NVMe storage is the component that will reap the most benefits from PCIe 4.0. NVMe SDD and AIC storage devices can benefit from both the greater throughput and the throughput available per lane in the current top-performing NVMe SDD and AIC storage devices.
Lanes
Each PCIe version increases bandwidth per lane, reducing the number of lanes required by newer devices. For example, even the most powerful graphics cards no longer require all 16 lanes to function properly. It frees up additional lanes for other vehicles by using fewer lanes. Due to the fact that CPUs have a limited number of lanes, they must be allocated across the many devices.
Xem thêm : What Is GDDR Memory? Which Version Of GDDR Should You Get? Update 07/2025
The same may be said for storing information in a computer. PCIe add-in card (AIC) adapters can connect more NVMe M.2 SSDs if your storage devices no longer require as many lanes.
Single lanes can now deliver 10 Gbps Ethernet on the network.
Future-Proofing
Upgrade to 4.0 may make sense when you’re putting together a new system. As a result, future graphics cards and storage devices may be able to utilize even more bandwidth. Take into account your projected duration of computer use in this situation. Will you, for example, spend the next few years upgrading your storage and graphics card, or will you opt to have the complete system replaced now?
PCIe 3.0 vs PCIe 4.0
This is a good moment for an update to PCIe 3.0, which was introduced in 2010. As far as I know, PCIe 4.0 offers how big of an increase in performance?
Every PCIe generation prior to this one has provided nearly two times the transfer speeds and bandwidth of the one before it, and this one is no different. Comparing PCIe 3.0 and 4.0 statistics, the scenario appears to be this:
PCIe 4.0 adds only a two-fold increase in transfer rates. It’s also worth noting that the only PCIe 4.0-compliant chipsets and CPUs are from AMD.
This means that, on paper, PCIe 4.0 is a clear winner, but it’s important to remember that high numbers on spec sheets don’t necessarily translate into better gameplay. What does this mean in practice, and is it worthwhile to purchase PCIe 4.0?
Is PCIe 4.0 Worth It In 2022?
Let’s get to the crux of the matter: Is PCIe 4.0 better for gaming?
In a nutshell, no, it does not, at least not much.
The video above illustrates how an RX 5700 XT performs in a PCIe 3.0 x16 slot compared to a PCIe 4.0 x16 slot when that same GPU is put in both slots. As you can see, there isn’t much of a distinction between the two.
There is no need to buy PCIe 4.0-compliant graphics cards and CPUs if you want greater in-game performance, as modern graphics currently have no requirement for the amount of bandwidth that PCIe 4.0 provides.
Similarly, when it comes to SSDs, PCIe 4.0 does offer an edge when it comes to gaming because it increases loading speeds, but the difference is so slight that you’d hardly notice it. Everyday computer use is the same.
When it comes to high-performance NVMe SSDs, PCIe 4.0 offers a noticeable gain because the extra bandwidth allows the SSD to read and write massive volumes of data more quickly. Of course, this isn’t an issue if you’re designing a gaming PC as opposed to a workstation.
You don’t have to worry about compatibility concerns with PCIe because it is both forward and backward compatible.
Although PCIe 4.0’s higher bandwidth and data transfer rates aren’t going to make much of a difference in terms of gameplay, they’re nevertheless easy to overlook on a gaming PC.
FAQS:
What Is the Latest Version of PCI-Express?
PCIe 5.0 is the most recent version of PCI-Express. Intel has PCIe 5.0 processors, but AMD only has PCIe 4.0.
Xem thêm : Best Graphics Card Brands & Manufacturers. Which Is Best For You? Update 07/2025
When it comes to CPU lanes, Intel’s 12th generation Core CPUs (either one with x16 or two with x8 PCIe slots) offer PCIe 5.0 support and PCIe 4.0/3.0 speeds for the rest of the system’s lanes.
The first AMD desktop CPUs to enable PCIe 5.0 are the Zen 4-based Ryzen 7000 models. After the second half of 2022, the Ryzen 7000 CPUs are projected to be available.
Formally referred to as PCIe Gen 3, Gen 4, and Gen 5, PCIe versions 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 are also known as PCIe Gens 3 and 4. PCI-third, Express’s fourth, and fifth generations are referred to as “generations 3 through 5.”
Graphics cards and storage devices that support PCIe 5.0 are not yet available for purchase.
How Fast Is PCIe?
The PCI-Express version and the number of lanes used determine the speed of PCI-Express. x1 refers to the first lane, x2 to the second, and so on. Technically, PCI-Express can provide x32 width. However, the following PCIe widths are available on the majority of consumer motherboards: x1, x2, x4, x8, and x16.
CPU lanes (i.e. one x16 or two x8 PCIe slots) are currently supported by PCIe 5.0 on Intel’s 12th generation CPUs, with the other lanes running at PCIe 4.0/3.0 speeds.
4 GB/s of bandwidth is available per PCIe 5.0 lane. A PCI-Express 5.0 x16 card with a capacity of 4 GB/s per lane can deliver up to 64 GB/s of throughput.
Because NVMe M.2 SSD cards employ two or four lanes, PCIe 4.0 provides 4–8 GB/s of bandwidth.
When compared to PCIe 4.0, PCIe 3.0 has only half the bandwidth.
Which Desktop and Workstation PCIe 4.0 CPUs Are Available?
There are a number of AMD CPUs that support PCIe 4.0, including AMD’s Ryzen 3000, 5000, and Threadripper 3000 series. PCIe 4.0 is supported by Intel’s “Rocket Lake” 11th generation processors.
Which Motherboards Support PCIe 4.0?
You’ll need one of the following motherboard chipsets to get full PCIe 4.0 functionality.
A motherboard with the Z590 or B560 chipset is required for full PCIe 4.0 functionality for Intel’s 11th generation processors.
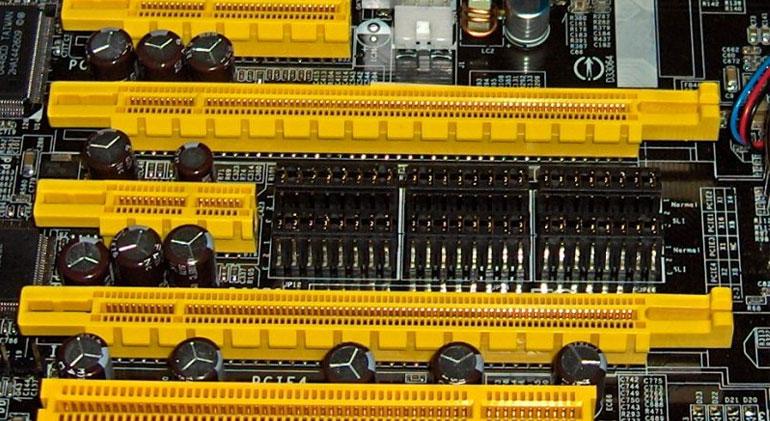

PCIe 4.0 support for AMD Ryzen processors requires the use of a motherboard with the X570 chipset. Ryzen 3000 and 5000 series CPUs require different motherboards.
The TRX40 chipset is required for full PCIe 4.0 functionality for AMD’s ThreadRipper processors.
Conclusion:
So, in the end, acquiring a PCIe 4.0-equipped motherboard for a gaming PC is a waste of money because it currently offers no actual benefits for GPUs or SSDs in terms of gaming and will take years to do so.
We hope you found this post useful, and as always, please let us know if there are any errors or omissions, and we’ll do our best to correct them as quickly as possible!
Nguồn: https://gemaga.com
Danh mục: Best










