Building a gaming PC from scratch can be a fun but time-consuming experience.
While it can be fun for hardware enthusiasts to compare benchmarks and read a variety of expert reviews before making a purchase, those who aren’t already well-versed in the field may find the information overwhelming.
Bạn đang xem: Cpu Hierarchy Update 03/2026
Finding the right central processing unit (CPU) doesn’t always require tedious research into various CPU models and a comparison of their respective specifications, benchmarks, and reviews.
Listed below is our gaming CPU hierarchy, in which both current-generation and previous-generation CPUs are ranked according to their performance in various games.
| CPU Model | Number of Core Threads | Typical Clock Rate (GHz) | Ability to Overclock | Socket |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i9-12900KS Intel Core i9 | 8 (16) | 3.4 | Yes | LGA 1700 |
| Core i9-12900K from Intel | 8 (16) | 3.2 | Yes | LGA 1700 |
| Core i9-12900 from Intel | 8 (16) | 2.4 | No | LGA 1700 |
| Core i7-12700K by Intel | 8 (16) | 3.6 | Yes | LGA 1700 |
| Core i7-12700 from Intel | 8 (16) | 2.1 | No | LGA 1700 |
| processor with Intel Core i5-12600K cores | 6 (12) | 3.7 | Yes | LGA 1700 |
| Core i9-11900K from Intel | 8 (16) | 3.5 | Yes | LGA1200 |
| i9-11900K Intel Core i9 | 8 (16) | 2.5 | No | LGA1200 |
| ATI Radeon Pro 5950X | 16 (32) | 3.4 | Yes | AM4 |
| Ryzen 9 5900X from AMD | 12 (24) | 3.7 | Yes | AM4 |
| Processor Type: Intel Core i5-12600 | 6 (12) | 3.3 | No | LGA 1700 |
| An Intel Core i7-11700K | 8 (16) | 3.6 | Yes | LGA1200 |
| Ryzen 7 5800X from AMD | 8 (16) | 3.8 | Yes | AM4 |
| CPU: Intel Core i7-11700 | 8 (16) | 2.5 | No | LGA1200 |
| Core i5-11600K by Intel | 6 (12) | 3.9 | Yes | LGA1200 |
| It uses a Core i5-12500 processor from Intel. | 6 (12) | 3.0 | No | LGA 1700 |
| Ryzen 5 5600X from AMD. | 6 (12) | 3.7 | Yes | AM4 |
| CPU: Intel Core i5-11600 | 6 (12) | 2.8 | No | LGA1200 |
| Core i5-12400 from Intel | 6 (12) | 2.5 | No | LGA 1700 |
| Powerful and Efficient Intel Core i3-12300 | 4 (8) | 3.5 | No | LGA 1700 |
| ATI Radeon 9 3950X | 16 (32) | 3.5 | Yes | AM4 |
| The AMD Ryzen 9 3900XT | 12 (24) | 3.8 | Yes | AM4 |
| Ryzen 9 3900X from AMD | 12 (24) | 3.8 | Yes | AM4 |
| processor with Intel’s Core i5-11500 cores | 6 (12) | 2.7 | No | LGA1200 |
| CPU: Intel Core i5-11400 | 6 (12) | 2.6 | No | LGA1200 |
| Core i3-12100 from Intel | 4 (8) | 3.3 | No | LGA 1700 |
| CPU: AMD Ryzen 7 3800XT | 8 (16) | 3.9 | Yes | AM4 |
| Ryzen 7 3800X from AMD | 8 (16) | 3.9 | Yes | AM4 |
| ATI Radeon 7 3700X | 8 (16) | 3.6 | Yes | AM4 |
| ATI Radeon 5 3600XT | 6 (12) | 3.8 | Yes | AM4 |
| Processor: AMD Ryzen 5 3600X | 6 (12) | 3.8 | Yes | AM4 |
| A 5 3600 from AMD | 6 (12) | 3.6 | Yes | AM4 |
| Ryzen 3 3300X from AMD | 4 (8) | 3.8 | Yes | AM4 |
| The AMD Ryzen 3 3100 | 4 (8) | 3.6 | Yes | AM4 |
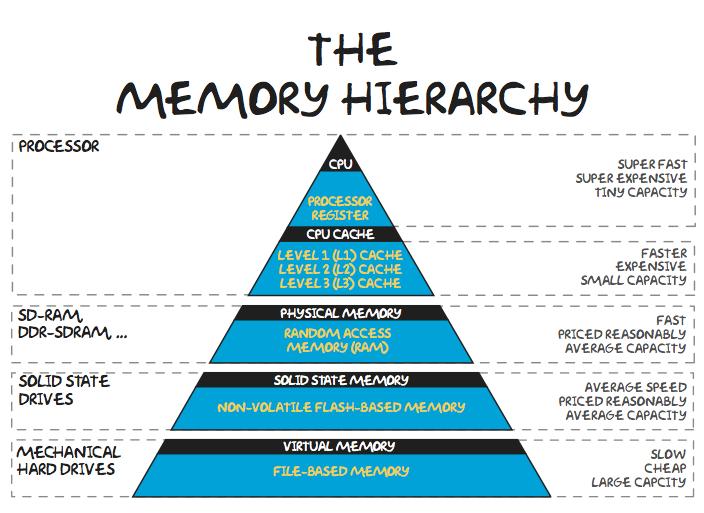
What Is CPU Hierarchy?
The CPU hierarchy, also known as the processor hierarchy, ranks various central processing units (brand, model, core, etc.) for various purposes (gaming, general usage, server/workstation, etc.) based on CPU benchmark.
Why Need to Classify CPU Hierarchy?
As a resource for computer users looking into upgrading their central processing units. We are all aware that the central processing unit significantly impacts a computer’s overall performance. The central processing unit is the brain of the computer. Choosing the right central processing unit is crucial.
Despite this, there are countless central processing units (CPUs) on the market boasting that they are superior, can accomplish xxx, are optimized for xxx, etc. It’s possible you’re feeling overwhelmed because you can’t decide which option is best for you. Then, with a CPU hierarchy in place, picking the right one is a breeze. That’s why having a set order to CPUs is essential.
Tier 1 — Enthusiast
These top-tier central processing units (CPUs) are the most potent CPUs available today. They have the most CPU cores and threads, and they usually have great overclocking potential; however, they are also the most expensive and power-hungry options.
These central processing units (CPUs) aren’t designed with gaming in mind, but they’re a good choice for people who want to run both games and CPU-intensive professional software on their PCs.
| AMD CPUs | CPUs by Intel |
|---|---|
| ATI Radeon Pro 5950X | Core i9-12900KS from Intel |
| Ryzen 9 5900X from AMD | i9-12900K Intel Core i9 |
| ATI Radeon 9 3950X | Core i9-12900 from Intel |
| CPU: AMD Ryzen 9 3900XT | i9-11900K Intel Core i9 |
| Ryzen 9 3900X from AMD | Core i9-11900 from Intel |
Tier 2 — High-End
If you also plan to purchase a high-end graphics processing unit, the processors in this tier are your best bet.
The aforementioned Ryzen 9 and Core i9 models are more expensive but offer comparable performance. They make the most of the strongest graphics processing units (GPUs) on the market and perform admirably with heavy-duty programs.
| AMD CPUs | CPUs by Intel |
|---|---|
| The AMD Ryzen 7 5800X | Core i7-12700K by Intel |
| System:AMD Ryzen 7 3800XT | Technology: Intel Core i7-12700 |
| ATI Radeon 7 3800X | i7-11700K Intel Core i7 |
| ATI Radeon 7 3700X | Core i7-11700 from Intel |
Tier 3 — Mid-Range
Xem thêm : Intel Xeon For Gaming Worth It Update 03/2026
We’ve reached the middle of the price spectrum, where you’ll typically find the best overall performance for your dollar. This is why mid-range CPUs are so widely used in gaming PCs.
To ensure that even the most powerful GPUs are not slowed down, mid-range CPUs in 2022 have higher core and thread counts than ever before, and they typically come with a very reasonable price tag.
| AMD CPUs | Microprocessors by Intel |
|---|---|
| ATI Radeon 5 600X | Core i5-12600K by Intel |
| A 5 3600XT from AMD | Core i5-12600 from Intel |
| Ryzen 5 3600X from AMD | CPU: Intel Core i5-12500 |
| ATI Radeon 5 3600 | Core i5-12400 from Intel |
| CPU: Intel Core i5-11600K | |
| The Intel Core i5-11600 | |
| Core i5-11500 Intel Processor | |
| The Intel Core i5-11400 |
Tier 4 — Budget
Finally, both Intel and AMD offer very viable budget-oriented solutions for those who are pinching pennies and cannot yet afford to spend a lot of money on a CPU or the PC as a whole.
When compared to more expensive CPUs, these lack not only the high core and thread counts, but also the impressive clock speeds and overclocking potential. However, they are cheap and represent the best value for money option for many low- to mid-tier gaming PCs. However, they are not very resilient to change in the future.
| AMD CPUs | CPUs by Intel |
|---|---|
| Ryzen 3 3300X from AMD | Chipset: Intel Core i3-12300 |
| ATI Radeon 3100 | Core i3-12100 from Intel |
What is a processor and what does it do for your computer?
A computer’s processor is its central processing unit. The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brains of the machine; it may have multiple “cores,” or smaller processors, each of which performs its own separate tasks.
A computer’s processor processes data and follows instructions from the computer’s motherboard. This involves tasks such as deciphering software instructions, running those instructions simultaneously on multiple data cores, and sorting through input/output requests from other components. If you want a more potent computer, you should get one with a faster central processing unit (CPU), which is responsible for carrying out these tasks.
Each person is responsible for their own “thread” or “job,” and while they are all busy, someone has to oversee their efforts to ensure everything gets done on time. Here, he is referred to as the Central Processing Unit (CPU).
The different types of processors:
The central processing unit (CPU) of your computer is the microprocessor that controls everything. It consists of a large number of smaller parts called cores, each of which performs a single function. If you need more muscle from your PC, you need a faster processor, and that is in turn determined by the number of cores it has.
There are four types of processors:
The central processing unit (CPU) is the “brain” of any computer.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) handles all graphics-related tasks for your PC and can have anywhere from one to hundreds of cores.
You can find digital signal processors (DSPs) in places like ATMs and cars, and they’re used for processing audio signals like voice recognition and music synthesis. They are quicker than CPUs because they can process many small chunks simultaneously.
Accelerated Processing Units (APUs) are a type of hardware that combines a central processing unit (CPU) with graphical processing capabilities and a video memory controller. This type of central processing unit (CPU) can handle both your machine’s graphics and computing needs.
Xem thêm : Genshin Impact Beginners Guide Update 03/2026
CPUs have evolved from supporting four cores to supporting up to 32 cores as a result of recent technological advancements. As for the number of cores, modern processors can have anywhere from eight to sixty-four. It’s worth it to spend a little more money on a high-end model like the Intel Core i7920X if you want a computer that never slows down. Your neighborhood computer shop should be able to help you choose the right processor based on your specific requirements.
How to choose the best processor for you?
Pick a CPU that can handle your workload effectively.
- The Intel Core i series and the AMD FX lines are better options than an expensive CPU like one of Intel’s Xeon processors or some of the high-end processors from AMD’s Opteron line if you’re doing heavy work but don’t need much raw power.
- Fast rendering times (again, not so important if what you’re rendering isn’t time-sensitive) can be achieved with a more powerful computer, such as a Xeon E5500, thanks to the processor’s Hyperthreading (the ability to perform multiple tasks at once).
- It’s useful for figuring out what kinds of applications you’ll be making. Again, a Xeon E5500 would be a better option than an Intel Core i series or FX processor if you plan on editing video or audio (video editing has traditionally been more about raw power than speed).
- Keep in mind that the latest processor from AMD’s Athlon line does not have Hyperthreading capabilities, so rendering times will be longer than with other processors, but it may be sufficient for your needs if they are limited to general office tasks and web browsing multi-tasking.
- Home users whose computing needs are limited to the usual suspects—word processing, gaming, streaming video from services like YouTube and Hulu—will benefit greatly from Intel Celeron processors.
- The Intel Core i series or AMD’s FX line are better if you’re an engineer who doesn’t need to do a lot of video editing.
Why CPUs are so important in modern-day computing?
Central processing units (CPUs) are the computational “neurons” of any device. I can’t overstate how crucial they are to the health of your electronics. They have a significant effect on the rate at which games run, files are encoded and played back, videos are edited, photos are manipulated, and even documents are written.
Which central processing unit should you buy? That’s why this article is so helpful. You can use this collection of central processing units to make a well-informed purchase decision. This is by no means an exhaustive list, but it does reflect some of the pros and cons of popular CPU upgrades (don’t ask me for specific recommendations, though). Some information about potential future processors is included as well.
The Final Word
Our gaming CPU hierarchy is now complete!
You may have noticed that none of the more expensive AMD Threadripper or Intel Core X models were included; this was done on purpose, as we do not consider them to be good choices for gaming. They are much more expensive than regular computers and have far more processing power than a gamer needs.
The same goes for cheaper entry-level solutions like AMD’s Athlon APUs or Intel’s Pentium and Celeron lineups, which we left out for the same reason: they aren’t great choices for gaming because they aren’t powerful enough to avoid significantly slowing down the most recent GPUs.
Now, we should also note that while Intel Core CPUs appear to be the clear winner for gaming, the CPUs were ranked based on gaming performance without also considering another important factor: value.
In this context, “value” refers to the ratio of a CPU’s price to its performance, and since this ratio can change depending on a wide variety of factors, including the difficulty and degree to which individual games have been optimized, it can be difficult to determine with precision.
Check out our curated list of what we believe to be the best CPUs for gaming in 2022 for more informed suggestions that go beyond pure gaming performance.
Finally, if you notice that any recent or older CPU generations are missing from the list, please let us know in the comments section below, and we will do our best to add them.
Nguồn: https://gemaga.com
Danh mục: Blog