Concerns about “OLED burn-in” have dogged OLED as a high-end TV technology since its inception. When pictures from the television, such as network logos and score boxes, are “burned in” to the television, it’s known as a “burn-in”.
- Animal Crossing: New Horizons Guide – How To Add & Remove Villagers? Update 02/2026
- What Are NVIDIA CUDA Cores? How Many CUDA Cores Do You Need? Update 02/2026
- How To Install A New Graphics Card Update 02/2026
- Are Sound Cards Worth It? Comprehensive Guide Update 02/2026
- Overwatch Zenyatta Guide: Helpful Tips and Strategies Update 02/2026
With LG offering “Screen Shift” and “Logo Luminance Adjustment,” and Sony offering “Pixel Shift,” the major manufacturers have attempted to minimize the potential harm. OLED screens in non-TV devices, such as smartphones and even the Nintendo Switch, which recently released a version with an OLED screen, may also be susceptible to burn-in.
Bạn đang xem: What Is OLED Burn-In? Comprehensive Guide Update 02/2026
What Is OLED And How Does It Work?
To begin, let’s quickly go over the fundamentals of OLED, namely what it is and how it works.
It stands for “organic light-emitting diode,” and it’s a display technology that’s considerably different from LCD, which is used in most modern televisions and monitors.

Unlike LCD, OLED does not use an active backlight and each pixel works as its own source of light. This means that an OLED display can be more power-efficient than an LCD one, and it can also deliver a lot greater contrast than an LCD panel could ever hope to achieve.
If you’re looking for a display that is more accurate in color, has a higher refresh rate, and responds more quickly, then OLED displays are the best option for you.
Burn-in is one of the main downsides of OLED, but what is it and how does it occur?
What Is OLED Burn-In?
As previously stated, each pixel in an OLED display serves as its own independent light source, however no piece of hardware lasts indefinitely, therefore the brightness of an OLED panel’s pixels will decrease over time.
It is possible to “burn in” a computer screen by wearing down and dimming only a small section of the screen’s pixels.
Xem thêm : What Graphics Card Do I Have? How to Buy a New Graphics Card? Update 02/2026
Long-running static visuals, such as TV channel logos or the Windows taskbar, are the most common cause of this problem. A unusually bright static image indicates that pixels in that area of the screen are more likely to degrade quickly than those around them.
Burn-in, on the other hand, is irreversible and cannot be reversed. Unlike, say, a li-ion battery, which loses its capacity over time, pixels are projected to lose brightness with time.
The risk of burn-in should be reduced wherever possible while using an OLED display, whether it’s an OLED screen on your phone or a TV or a monitor.
How To Prevent OLED Burn-In
To avoid burn-in on OLED screens due to static, bright images, keep the foregoing in mind: don’t display them for lengthy periods of time. It can range from a few hours to several days when we mention “extended spans of time.”
If you want to extend the life of your OLED display, screensavers and dark mode are your greatest friends. If you’re going to be staring at the screen for an extended period of time, consider turning down the brightness. It’s also a good idea to switch off the display while it’s not in use.
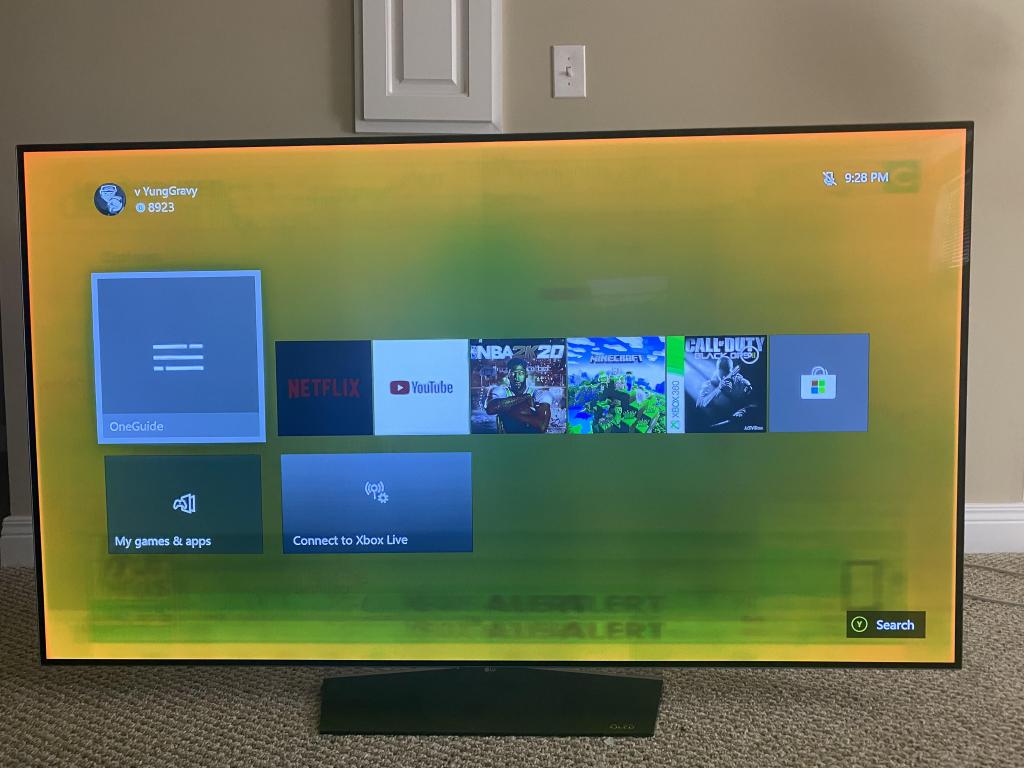
There is a difference between burn-in and image retention. Displays that show static images for a lengthy period of time may result in a “ghost” of the picture remaining even after it is no longer visible. Unlike burn-in, this type of picture retention will fade away on its own over time and is not permanent.
Even more encouraging, OLED TV manufacturers incorporate capabilities that can assist avoid unwanted pixel wear-and-tear. To avoid burn-in, the display may, for example, determine which pixels are showing a static image and then refresh them frequently or automatically reduce their brightness to a given degree.
How to avoid OLED burn in
You can engage a number of various modes in your TV’s Settings menu to assist prevent burn-in:
Pixel Shift
Your TV’s pixels are shifted in an extremely imperceptible manner when static information is detected by this technology.
This prevents the pixels in your display from burning in when you show the same image over an extended period of time.
Screen saver
Xem thêm : Steam Client Running Slow? Comprehensive Guide Update 02/2026
The default screen saver setting on some TVs is either a subtle animation (LG’s is fireworks on a black screen) or a constant movement of the pixels to prevent them from burning in.
Smart gadgets, such as the new Apple TV 4K, can also be used to trigger a screen saver.
Pixel wash
TVs with a burn-in treatment feature selectively wash the pixels to treat afterimage and prevent burn-in are available.
After a period of time, some TVs even do it automatically as part of a maintenance routine.
FAQS:
Can burn-in be fixed OLED?
This isn’t a constant issue, but it may pop up every now and again. Rather of becoming permanent burn-in, it is more likely that it will fade away on its own. In the good news, there are many ways to repair this and prevent picture retention or the potential of burn-in from occurring in the future.
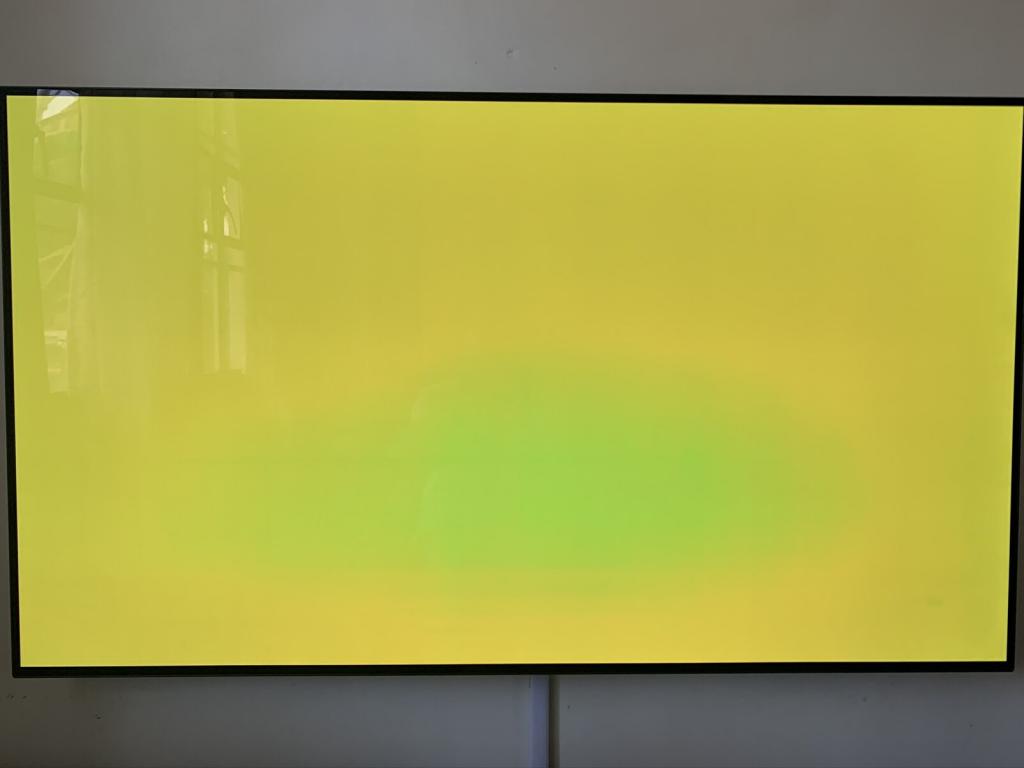

How does OLED burn-in happen?
On any display, there is the potential for burn-in and picture retention…. Most incidents of burn-in in televisions are caused by the display of static images or on-screen features for long periods of time, with the brightness normally at its highest.
Conclusion:
You now know exactly what OLED burn-in is and how to avoid it.
When it comes to smartphones with OLED displays, you don’t have to worry about burn-in because you’ll likely take regular pauses from using it, enabling the pixels to cool down. You’ll probably obtain a new phone long before any serious burn-in is visible because it normally takes years for the first signs of burn-in to develop.
OLED TVs and monitors can be expensive, so taking care of them and preventing burn-in is a must if you plan on purchasing one.
OLED monitors are now excessively expensive, and they primarily appeal to specialists who need the most accurate color reproduction possible. Many less expensive options are available for gamers who want to get the most out of their gaming experience without breaking the bank (no pun intended).
Nguồn: https://gemaga.com
Danh mục: Guide